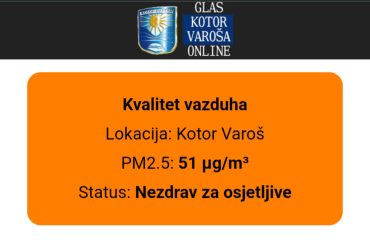
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) from the USA has conducted the largest study to date providing evidence of the link between air pollution and dementia. Airborne particles known as PM2.5 damage brain tissue and increase the risk of developing dementia.
Every increase of 10 µg/m3 in the concentration of PM2.5 particles raises the risk of dementia by as much as 14%.